题目描述
在的棋盘上,摆有八个棋子,每个棋子上标有至的某一数字。棋盘中留有一个空格,空格用来表示。空格周围的棋子可以移到空格中。要求解的问题是:给出一种初始布局(初始状态)和目标布局(为了使题目简单,设目标状态为),找到一种最少步骤的移动方法,实现从初始布局到目标布局的转变。
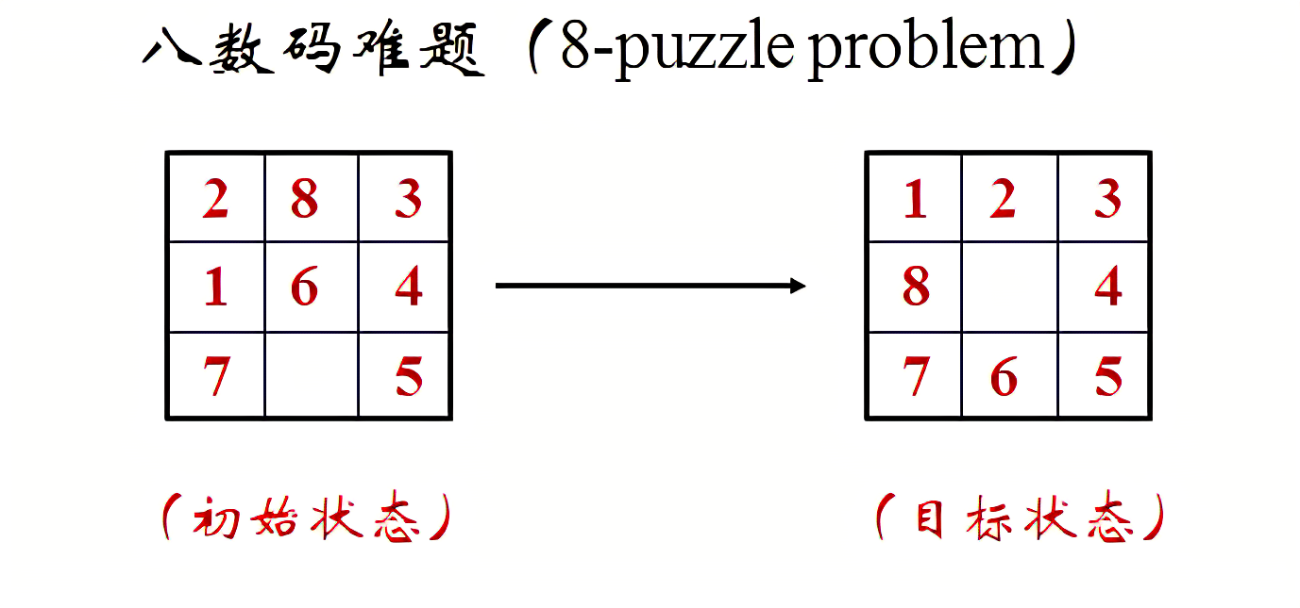
输入输出样例
input1:
output1:
input2:
output2:
input3:
output3:

问题分析
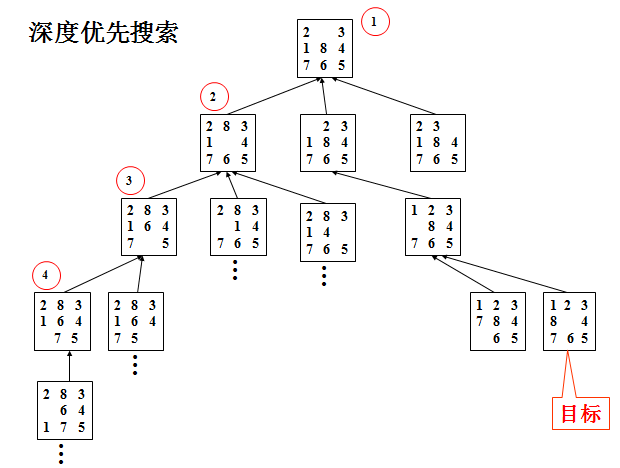
朴素BFS
看完问题我们最先想到的一定是BFS,因为我们知道起始状态和目标状态,且不需要求解过程,只需要知道执行的步骤,那么DFS自然就不需要了。因此最简单的办法就是套用BFS模板,目标状态的深度即为答案。过程很简单,看代码就可以理解的哈,不理解可以温习一下BFS的原理:BFS简介
朴素BFS代码
int main()
{
string start;
int depth=0;
queue<string> Q;
Q.push(start);
while(!Q.empty())
{
int len=Q.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)//while循环内的for循环代表树的深度
{
string node=Q.front();
int position;//数字0的位置
if(node[j]=='0')//寻找数字0在九宫格的位置
position=j;
if(position == 1,2,4,5,7,8)//数字0向左移动
{
swap(node[position],node[position-1]);//与0交换位置
Q.push(node);
judge();//判断是否是目标状态
swap(node[position],node[position-1]);//交换回来
}
if(position == 3,4,5,6,7,8)//数字0向上移动
{
swap(node[position],node[position-3]);//与0交换位置
Q.push(node);
judge();//判断是否是目标状态
swap(node[position],node[position-3]);//交换回来
}
if(position == 0,1,3,4,6,7)//数字0向右移动
{
swap(node[position],node[position+1]);//与0交换位置
Q.push(node);
judge();//判断是否是目标状态
swap(node[position],node[position+1]);//交换回来
}
if(position == 0,1,2,3,4,5)//down
{
swap(node[position],node[position+3]);//与0交换位置
Q.push(node);
judge();//判断是否是目标状态
swap(node[position],node[position+3]);//交换回来
}
Q.pop();
}
depth++;
}
}记忆化BFS搜索
但是,这样的搜索显然是有很多重复的节点,会出现返祖现象,就是说后面的搜索包含了前面已经搜索过的节点。比如,数字0第一次向右移动,第二次向左移动,就相当没移动,又回到原来的节点了。那么为了避免这个问题,我们使用一个超大的数组来记录每一次遍历过的节点状态,因为BFS是按照层级顺序搜索的,因此每次搜索前查找一下这个超大数组,如果已经遍历过的节点将不会再次遍历。这样的减枝可以极大的提高搜索效率,可以减少大约50%的重复搜索时间。
记忆化BFS搜索代码
string disk[1000001];//记忆数组
int main()
{
string start;
string final="123804765";
int depth=0;
int ptr=0;
queue<string> Q;
disk[0]=start;
Q.push(start);
while(!Q.empty())
{
int len=Q.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
string node=Q.front();
int position;//数字0的位置
if(node[j]=='0')//寻找数字0在九宫格的位置
position=j;
if(position == 1,2,4,5,7,8)//数字0向左移动
{
swap(node[position],node[position-1]);
//----------------------
bool judge=true;
for(int j=ptr;j>=0;j--)//从后向前检查该节点是否遍历过
if(disk[j]==node)
{
judge=false;
break;
}
if(judge)//如果没有遍历过
{
Q.push(node);
ptr++;
disk[ptr] = node;
if(node==final)
{
cout<<depth+1<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
//---------------------
swap(node[position],node[position-1]);
}
if(position>2)//数字0向上移动
{
swap(node[position],node[position-3]);
//同上
swap(node[position],node[position-3]);
}
if(position == 0,1,3,4,6,7)//数字0向右移动
{
bool judge=true;
swap(node[position],node[position+1]);
//同上
swap(node[position],node[position+1]);
}
if(position<6)//数字0向下移动
{
swap(node[position],node[position+3]);
//同上
swap(node[position],node[position+3]);
}
Q.pop();
}
depth++;
}
}双向BFS
虽然上述方法已经很快了,但是执行依旧需要将近20秒的时间,因此当节点很深的时候,我们有没有更快的办法呢?
对于本题而言,双向BFS就派上用场了,因为本题已知起始状态和目标状态,我们完全可以同时对这两个状态进行BFS,当两面搜索到了同一个节点时,两面的深度之和就是答案。如图所示,同样的,对于一些走迷宫类的问题,给出起始状态和中止状态,我们都可以考虑使用双向BFS来求解。这种方法有多快呢, 对于而言,使用双向BFS求解的时间仅需,是单向BFS速度的近百倍!
这里,我们对代码进行了一些小小的优化,将原本的disk数组更换成了更高效的哈希映射,通过康托展开将的全排列一一映射到大小仅为的哈希表中。或许你会疑惑,原本应该至少需要开disk[876543210]这么大的数组,怎么只需要disk[362880]就可以储存的下呢?我们来看一下康托展开的具体实现方式:康托展开_百度百科 (baidu.com).
是不是很神奇呢?
双向BFS代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct ant
{
string str;
int depth;
short one_two;
};
int visit[362880];
int depth[362880];
void bfs(string begin, string end);//双向BFS
int hash1(string s);//康托展开
int main()
{
string final = "123804765";
string start ="603712458";
bfs(start, final);
return 0;
}
int hash1(string s)//康托展开
{
int f[9]={0,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320};
int book[9]={0};
int ans=0;
int x=s.length();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
int num=0;
book[s[i]-'0']=1;
for(int j=0;j<s[i]-'0';j++)
if(!book[j])
num++;
x--;
ans+=num*f[x];
}
return ans;
}
void bfs(string begin, string end)
{
queue<ant> Q;
ant temp;
int str_to_int;//哈希转换
temp.str = begin;
temp.depth = 0;
temp.one_two = 1;//1代表正向BFS
Q.push(temp);
str_to_int = hash1(temp.str);
visit[str_to_int] = 1;
//depth[str_to_int] = 0;
temp.str = end;
temp.depth = 0;
temp.one_two = 2;
Q.push(temp);
str_to_int = hash1(temp.str);
visit[str_to_int] = 2;//2代表反向BFS
//depth[str_to_int] = 0;
while (!Q.empty())
{
ant node = Q.front();
node.depth++;
int position = -1;//position是数字0所在的位置
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
if (node.str[i] == '0')
{
position = i;
break;
}
if(position == 1,2,4,5,7,8)//数字0向左移动
{
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position - 1]);
str_to_int = hash1(node.str);
if (!visit[str_to_int])//没有访问过
{
Q.push(node);
visit[str_to_int] = node.one_two;
depth[str_to_int] = node.depth;
}
if(visit[str_to_int] + node.one_two == 3)//一个是1,一个是2,代表相遇
{
int ans = depth[str_to_int] + node.depth;
cout << ans << endl;
return;
}
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position - 1]);
}
if (position >= 3 && position <= 8)//数字0向上移动
{
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position - 3]);
str_to_int = hash1(node.str);
if (!visit[str_to_int])//没有访问过
{...}//同上
judge();//同上
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position - 3]);
}
if(position == 0,1,3,4,6,7)//数字0向右移动
{
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position + 1]);
str_to_int = hash1(node.str);
if (!visit[str_to_int])//没有访问过
{...}//同上
judge();//同上
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position + 1]);
}
if (position >= 0 && position <= 5)//数字0向下移动
{
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position + 3]);
str_to_int = hash1(node.str);
if (!visit[str_to_int])//没有访问过
{...}//同上
judge();//同上
swap(node.str[position], node.str[position + 3]);
}
Q.pop();
}
}A*算法
A*算法代码

